Injecting a liquid into a center pivot is an effective way to deliver nutrients to crops later in the growing season. Getting a fertigation or chemigation system setup is pretty straightforward, but there are some key aspects that you must get right to avoid any issues.
So if you are not familiar with the type of pump you need, not to mention the other components that make it all work, this article will give you the information you need. Let's get to it.
Components Needed for Injecting Fertilizer or Chemical into a Center Pivot Irrigation System
The main components needed to inject fertilizer are the pump, check valves, hose, strainer, and tank. Several types will work as long as they meet the necessary size, flow, and compatibility requirements.
- Positive Displacement Pump
- Check Valve
- Tank
- Hose/Plumbing
- Strainer
It is important to note that in addition to the fertilizer components we discuss in this guide, you also need a chemigation backflow preventer or check valve on the well. The fertilizer is injected downstream from this valve. The specifics are dictated by local regulations. This chemigation check valve prevents chemicals or fertilizer from getting into the well and contaminating groundwater.

These chemigation check valves are not sold by Dultmeier sales. For more information, you can check out this article from North Dakota State University. You can also check with your pivot dealer.
Injection Pump for Fertigation or Chemigation
If you want to apply fertilizer or chemicals through a center pivot you need a pump. That may be obvious, but you cannot use just any type of pump. While centrifugal pumps are commonly used to transfer fertilizer they will not be effective when it comes to injecting fertilizer into a pivot or any other irrigation pipe.
You need a positive displacement pump to inject liquids into the center pivot or irrigation pipe. This is a type of pump that uses mechanical means to physically move it fixed amount of fluid with each stroke or rotation. These pumps create higher pressure and central pumps and they can overcome the existing pressure in the irrigation line.
There are different types of positive displacement pumps. Piston pumps are commonly used when injecting into an irrigation line but a diaphragm pump can also be used. These injection pumps are rated in gallons per hour. In addition to moving the liquid, the pump also serves as the metering device.
These pumps can deliver a precise amount of liquid into the irrigation pipe, consistently with each stroke. The rate can be adjusted according to the amount of liquid you need to apply.
Irrigation Injection Pump Options

EZ Meter Piston Pumps
- Available in 5-30 GPH or 10-100 GPH
- Up to 150 PSI
- Wettable parts made of stainless steel and polypropylene, Teflon available
- Motors available in 12-volt, single-phase 110-220 volt, and three-phase 220-440 volt
- Easily repairable
View all the options EZ Meter pump options here.
Check Valve
We already talked about the chemigation check valve in the irrigation line to prevent backflow into the well. There is another check valve that is needed for the fertigation system. This is installed in the injection port. They ensure fertilizer is released in the center of the pipe, providing even dispersion.

These ensure only fertilizer gets in and nothing leaks when the pump is not running. They also provide back pressure to ensure the pump meters are accurate.
Storage Tank
The tank is pretty straightforward whether you are using a stationary tank or you have a nurse trailer, you must have a vessel to hold your fertilizer. Flat-bottom vertical storage tanks are very common and they are rated to handle heavy fertilizers.
Poly Vertical Tanks Tanks for Fertigation:
Hose/Plumbing
The hose that you use might seem like an afterthought, but the wrong hose could give you a lot of trouble. Just like with the pump, the hose needs to be constructed of material compatible with the fertilizer you are using. For nitrogen fertilizers, EPDM rubber hose works great.
You will need a reinforced suction hose on the inlet side of your pump. This means that from the supply tank to the pump. This hose should also have an inside diameter that is at least the size of the pump inlet. Using a smaller diameter hose can restrict the flow to the pump, damaging the pump and keeping you from hitting your application rate.
The discharge hose does not need to be rated for suction. It should be rated to handle some pressure, the EZ Meter pumps from John Blue can produce 150 PSI. The nature of how these pumps operate does create pulsing. This means that your discharge hose will jump around a bit. So be sure it won't rub on anything that could wear a hole in it during operation.
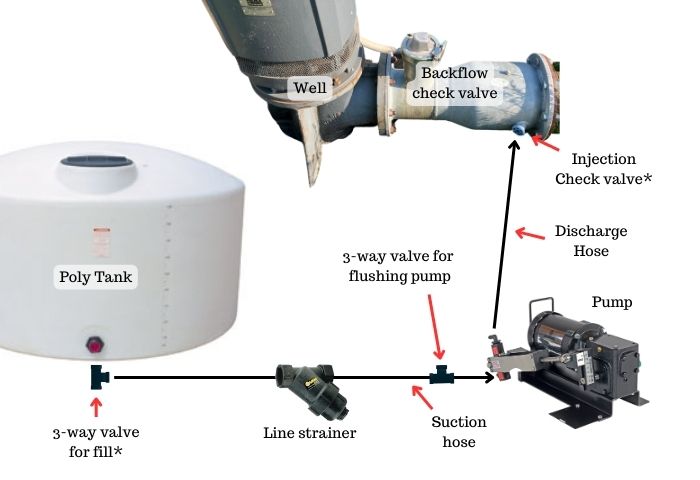
This is a typical plumbing diagram for injecting metering pumps.
Rinsing the pump is important. You can make it easier to do this by installing a 3-way valve somewhere in the suction line. This would allow you to switch from the fertilizer tank to a freshwater source. You can also use a three-way valve in the outlet of the tank so you can both withdraw and fill the tank without disconnecting the pump.

Filters
It is also vital to use a strainer in the suction line. This strainer should also be at least the size of the inlet port on the pump. A piston pump does not handle solid particles well, so the screen should have a fine mesh. The manufacturer of our piston pumps, John Blue, recommends an 80 mesh screen size to protect the pump.
Final Thought
With the right equipment and setup, you can deliver the nutrients your crops need through your irrigation system. Remember that the correct pump is vital to achieving the accurate results you want. Plumbing things correctly will help prolong the life of the pump and save you time.

Tech Ag & Industrial Sales
Shane Blomendahl is a tech sales veteran at Dultmeier Sales with over 10+ years of experience in liquid handling products covering several industries and applications.












